Background
In the past twenty years, supercritical fluid extraction technology has attracted considerable attention from researchers for its potential applications as an environmentally-friendly solvent for chemical processing, see Kiran and Levelt (1994) and McHugh and Krukonis (1994). Supercritical fluids (SCF) exhibit liquid-like solvation capabilities and gas-like mass and momentum transfer properties. Because of their high diffusivities, SCFs are capable of penetrating into porous solid 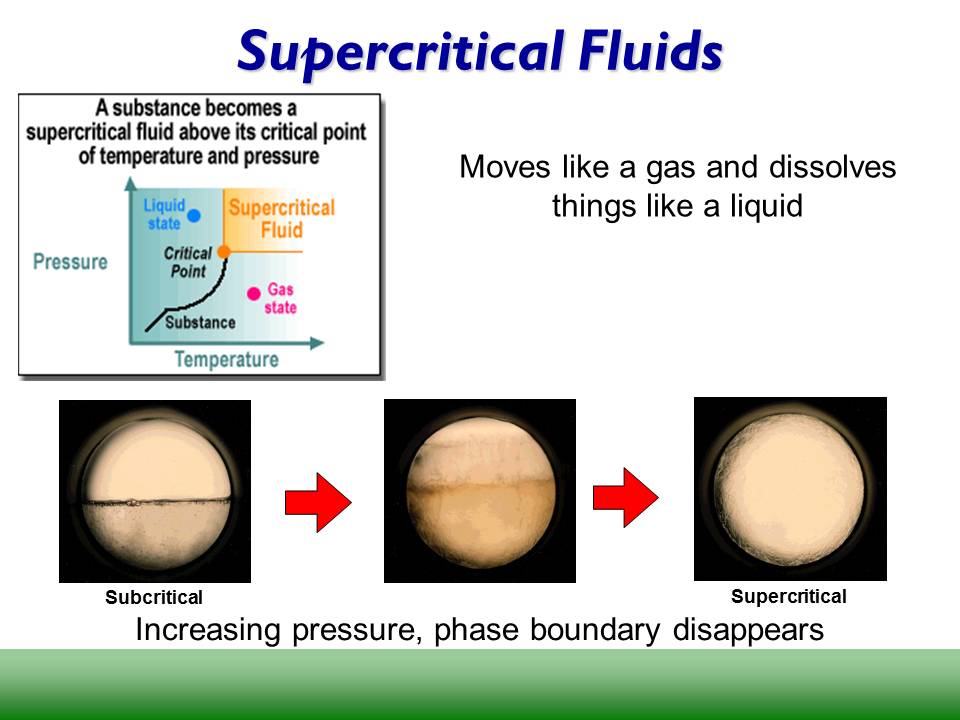 materials dissolving organic compounds. Because of their low viscosities, SCFs can be transferred in pipelines and pumped to high pressures requiring less mechanical energy than liquids and subcritical gases. Because the density of an SCF can be altered continuously by manipulating pressure and temperature, the solvation ability of the fluid is tunable. Thus, selective dissolution of solutes in a SCF may be achieved by optimizing the density of the fluid phase. This tunable solvation characteristic is a unique property that makes SCFs different from conventional liquid solvents. The other important advantage of SCF extraction is rapid separation of solutes that can be easily achieved by a reduction of pressure. Examples of large-scale commercial applications of the supercritical fluid extraction technology include crystallization, Hu et al. (2004), extraction of vitamins, natural flavors, perfumes, and essential oils from fruits and plants, Mansoori et al. (1988) and Martinelli et al. (1991), removal of unwanted materials, such as caffeine and cholesterol from food products, Mohamad and Mansoori (2000), and pollution remediation using environmentally friendly supercritical fluids Ekhtera et al. (1997).
materials dissolving organic compounds. Because of their low viscosities, SCFs can be transferred in pipelines and pumped to high pressures requiring less mechanical energy than liquids and subcritical gases. Because the density of an SCF can be altered continuously by manipulating pressure and temperature, the solvation ability of the fluid is tunable. Thus, selective dissolution of solutes in a SCF may be achieved by optimizing the density of the fluid phase. This tunable solvation characteristic is a unique property that makes SCFs different from conventional liquid solvents. The other important advantage of SCF extraction is rapid separation of solutes that can be easily achieved by a reduction of pressure. Examples of large-scale commercial applications of the supercritical fluid extraction technology include crystallization, Hu et al. (2004), extraction of vitamins, natural flavors, perfumes, and essential oils from fruits and plants, Mansoori et al. (1988) and Martinelli et al. (1991), removal of unwanted materials, such as caffeine and cholesterol from food products, Mohamad and Mansoori (2000), and pollution remediation using environmentally friendly supercritical fluids Ekhtera et al. (1997).
In 2003, and as a consultant, he prepared a special presentation for the AFRL titled as "Supercritical Fluids and Nanotechnology: Opportunities for Multidisciplinary Collaborative Research" to further motivate and encourage collaboration between scientists with variety of backgrounds. A table of content of this presentation is shown below.
Advanced Technology Consultants has since been involved in a number of consulting work pertaining to supercritical fluids such as cleaning opportunities in micro and specifically nanostructured materials.
Dr. Chehroudi has been as an invited author in a special volume of the Combustion Science and Technology Journal in 2006. The objectives of this paper was to bring to the attention of the scientific community opportunities for multidisciplinary research using SCFs, in particular, those that exist at the interface of SCF technology and nanotechnology due to their intrinsic overlap. The natural blending of supercritical fluids and nanotechnology has been made clear in this article. It was also the author’s intention to stimulate further investigations into applications of SCFs. This paper was not meant to be a comprehensive review and analysis of the current state of the art in SCF technology, but rather a concise overview of some selected current and emerging applications. In this article, the historical birth and importance of nanoscience are described followed by a concise presentation to understand special properties of SCFs. Then, examples on selected applications of SCFs in areas of propulsion, green chemistry, lithography, and materials are given. Later, close attention was paid on the application and synthesis of nanoparticles due to their importance in nano-science and technology as building blocks. Only nanoparticle manufacturing methods that employ special properties of the SFCs were presented. Later, the important role of SCFs in polymer industry is magnified. A few emerging applications at the interface of the SCF and nanotechnology are described. This paper ends with future trends, summary and conclusions.
NOTE: Contact Advanced Technology Consultants for consulting needs and opportunities in this area
_____________________________________________________________________________________
The following technical review article appeared as an invited paper in an special volume of the Combustion Science and Technology Journal dedicated to supercritical fluids and their applications. For a list of this and other papers click here: CST Journal.
Supercritical Fluids: Nanotechnology and Select Emerging Applications
Chehroudi, PhD
20 San Sovino
Newport Coast, CA 92657
An Invited Contribution
To An Special Volume of The Combustion Science and Technology Dedicated to Supercritical Fluids
(Volume 178, Numbers 1-3, Number 1-3/January 2006, pp. 555-621(67))
Source: Combustion Science and Technology. Publisher: Taylor and Francis Ltd
In this paper, a selected list of emerging applications of supercritical fluids (SCFs) are presented. In particular, demonstrated facts for the promise of the nanoscale science and technology and its overlap or interface with the SCFs technology are presented. It is argued that nanoengineered materials at the nanoscale have mechanical, optical, chemical, and electrical properties quite different from the bulk material. Examples of enhanced performance of many such materials when they are used in practical applications are given. SCFs, in particular carbon dioxide, on account of their special properties such as zero surface tension, low viscosity, and high solubility, enable them to play a critical role in many advanced technology applications. For example, as miniaturization efforts approach the nanoscale, surface tension forces become an important factor in many nanotechnology processes such as lithography in the electronic industry. In particular, the zero-surface-tension property of the SCFs presents them as a natural choice for nanotechnology processes. Cases are presented where SCF technology could enhance the advancement of nanotechnology or when the two technologies could have synergistic contributions to the synthesis and design of new materials and possibilities are presented. For example, advances in nanoscience and supercritical fluids have contributed to a better design and understanding of the composition, size, and structure of catalysts, crystals, sol-gels and composite material performance.
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Nano-science and technology (Significance, Classification, and Applications)
- What is a supercritical fluid (SCF) ?
- Selected emerging applications of SCF
- Propulsion
- Environmental issues (Green Chemistry)
- Solvent-free cleaning
- Lithography in semiconductor industry
- Material synthesis (Nanoparticles)
- Nanoparticles: applications
- Combustion and fuels
- Sol-Gel Chemistry
- Monopropellants
- Catalysis
- Material
- Biomedical
- Medical
- Nanoparticles: Synthesis using SCF
- Rapid expansion of supercritical fluid solution (RESS)
- Supercritical antisolvent method (SAS)
- Nanoparticles in SCF and reverse micelle
- Supercritical fluids and polymers
- Other emerging applications
- Nanoparticles: applications
- Some future trends in nanotechnology
- Future of supercritical fluids in nanotechnology and other emerging areas
- Summary and conclusions
- References
- Acknowledgement
- Appendix
Dr. Chehroudi was an Invited Speaker to Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH) for a presentation on Supercritical Fluids and Injection Processes of Relevance to High-Pressure Combustion, Colloquium in Thermo-Fluid Dynamics (Kolloquiums Thermo- und Fluiddynamik).
For a copy of Dr. Chehroudi's presentation click on the image below:
Supercritical Fluids and Nanotechnology
Click to see
Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL)
March 10, 2003
The following links provide information on use of supercritical injection in automotives:
- Transition of diesel spray to a supercritical state under engine conditions
- Supercritical and transcritical real-fluid mixing in diesel engine applications (Stanford University)
- On the transcritical mixing of fuels at diesel engine conditions
- Use of Supercritical Diesel Fuel for Improved Efficiency and Reduced Emissions
- Dieseline for Supercritical Injection and Combustion in Compression-Ignition Engines
- High-Pressure Supercritical Fuel Injection at Diesel Conditions
- Application of Supercritical Gasoline Injection to a Direct Injection Spark Ignition Engine for Particulate Reduction
- Fuel-injection System That Delivers 64 Miles Per Gallon
- Supercritical Fuel Injection | MIT Technology Review
- Transonic Supercritical Fuel Injection Could Improve Gasoline Engines by 50-75 Percent
- Supercritical fuel injection and combustion
- Transonic Combustion - A Novel Injection-Ignition System for Improved Gasoline Engine Efficiency
- Supercritical Fuel Injection System by NASA
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transonic_Combustion
- Supercritical combustion
NOTE: Contact Advanced Technology Consultants for consulting needs and opportunities in this area.




